|
|
||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | i | j | k | l | m | n | o | p | q | r | s | t | u | v | w | x y z | #
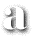
A2 envelope:
An envelope used for notecards, as opposed to a #10 envelope, which is a business-size envelope used in the U.S.A4 size:
The standard-size document used in Europe, slightly larger than the U.S. standard size of 8.5 x 11 inches.AAs:
Author's Alterations. Changes in copy or artwork after it has been typeset and sent to the printer. The additional costs incurred by AAs are charged to the client, not the printer.ABA:
American Booksellers Association. A trade association of publishers and booksellers.ABI:
Advance Book Information form. A form filed by publishers with R.R. Bowker/Reed Reference Publishing, which is used to list the book in directories such as Forthcoming Books and Books In Print.absorption:
The property that causes paper to take up liquids or vapors, such as the ability of a certain type of paper to absorb a certain type of ink.accordion fold:
Two or more parallel folds in printed paper in which each fold opens in the opposite direction from the previous fold so that the paper opens like an accordion.acid-free paper:
Paper that contains no acid or acid-producing chemicals, which cause it to yellow.acknowledgment:
A part of a book's front matter, in which the author expresses appreciation and thanks to the individuals and organizations who helped with the book.acquisition editor:
A person in a publishing house who is responsible for acquiring new titles.active matrix display:
In computer monitors, a type of LCD (liquid crystal display) that offers higher quality than a passive matrix display.additive color:
Color produced by combining red, green, and blue light in varying intensities. Computer monitors use additive color, while the printing process uses subtractive color. This causes inconsistency between what a designer sees on the monitor and what comes off the printing press.address:
In the online world, the combination of letters, numbers, and/or symbols that will let you send e-mail to a particular person or organization.advance:
Money paid to an author, usually at the time a contract is signed, that is a portion of expected royalties that will be paid to the author once the book is published. Originated from the phrase "advance against royalties."afterword:
Part of a book's back matter in which the author or publisher offers parting remarks to the reader.against the grain:
Folding or printing that is done at right angles to the grain direction of the paper. See grain.agate:
A unit of measure used in calculating columns of advertising space, primarily in newspapers. Fourteen agate lines equal one column inch.agent:
A person who represents an author by showing the author's manuscript to prospective publishers, handling contract negotiations, helping to sell subsidiary rights, and managing the author's business and financial transactions.airbrush (noun):
A small, high-pressure gun that sprays dye, used in retouching (or airbrushing, verb) photographic images.airbrush (verb):
To retouch photographic images with dye sprayed from a small, high-pressure gun (also known as an airbrush, noun). Similar retouching can be performed digitally with the use of image-manipulation software.ALA:
American Library Association. The largest library association in the United States.anthology:
A collection of writings by one or more authors, published as a single work.anti-alias:
In digital typography, the manipulation of gray levels around the edges of a letterform to minimize its jagged appearance when shown on-screen or output at low resolutions.anti-halation backing:
A coating applied to the back of a piece of film to prevent halation. See halation.anti-offset spray:
A dry or liquid spray used to prevent wet ink from transferring from one sheet of paper to another.antiquarian bookseller:
A bookseller who specializes in old or rare books.antique finish:
A type of surface, usually on books, that has a natural, rough finish.AOL:
America Online. A commercial information service with a graphical interface.appendix:
The part of a book's back matter that includes lists of resources, tables, or other reference material.Archie:
An Internet search tool for finding files and programs located on FTP servers.artifact:
A visible defect in a scanned image, usually caused by hardware or software limitations.artwork:
Any portion of a published piece that is not text.ascender:
The portion of a letter that rises above its x-height (the height of a lowercase "x" in a particular typeface).ASCII:
American Standard Code for Information Interchange. An ASCII file is one that contains text only, as opposed to an electronic file that contains text and graphics.as-told-to:
A book produced by a writer in collaboration with a non-writer, usually a celebrity.author's alterations:
Changes in copy or artwork after it has been typeset and sent to the printer, often called AAs. These types of changes frequently cost extra; the additional costs incurred by AAs are charged to the client, not the printer.automatic image replacement:
A process in which low-resolution FPO (For Position Only) images are automatically replaced by high-resolution images before outputting the final pages.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||